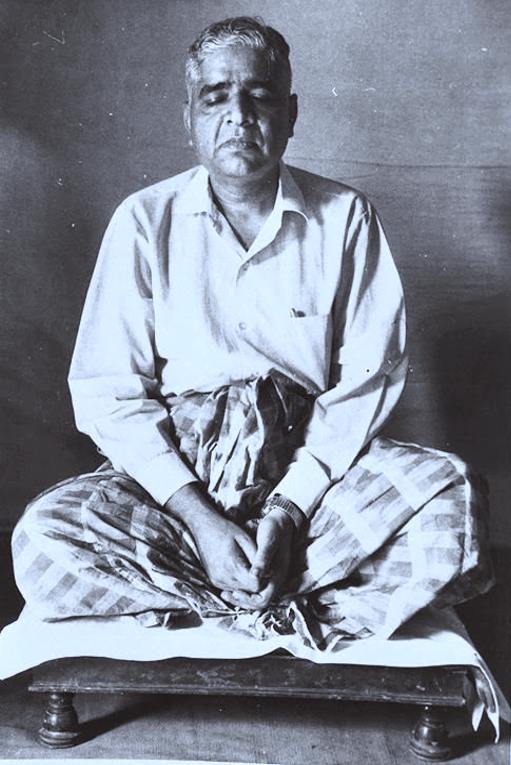
Buddhist meditation refers to the mental practices associated with the religion and philosophy of Buddhism. It is a means of training the mind and cultivating mindfulness, concentration, and other positive qualities. Buddhist meditation techniques have been developed and practiced for over 2500 years and can be found in a variety of traditions throughout the Buddhist world.
Here are some common styles of Buddhist meditation and brief descriptions of each:
- Mindfulness meditation: This involves focusing the mind on the present moment, usually through the sensation of the breath or bodily sensations. The goal is to cultivate a sense of clarity, non-judgment, and acceptance of whatever arises in the present moment.
- Loving-kindness meditation (metta): This involves cultivating feelings of love and well-wishing towards oneself and others. It involves silently repeating phrases of well-wishing and love to oneself and others, with the goal of cultivating positive states of mind and promoting feelings of connection and compassion towards all beings.
- Insight meditation (vipassana): This involves bringing a clear, non-judgmental attention to the present moment and exploring the nature of the mind and body. The goal is to gain insight into the impermanent, interconnected, and ultimately unsatisfactory nature of all phenomena.
- Concentration meditation (samatha): This involves focusing the mind on a single object, such as the breath or a mantra, with the goal of cultivating a calm and focused mind. This can be a helpful foundation for other forms of meditation and can lead to states of deep concentration and mental clarity.
- Tibetan Buddhist meditation: Tibetan Buddhism incorporates a wide range of meditation practices, including mindfulness, loving-kindness, and concentration meditation, as well as visualization practices and the use of mantras.
These are just a few examples of the many styles of Buddhist meditation that are practiced around the world. It is important to find a style of meditation that resonates with you and to work with a qualified teacher or guide to ensure that you are practicing in a safe and beneficial way.