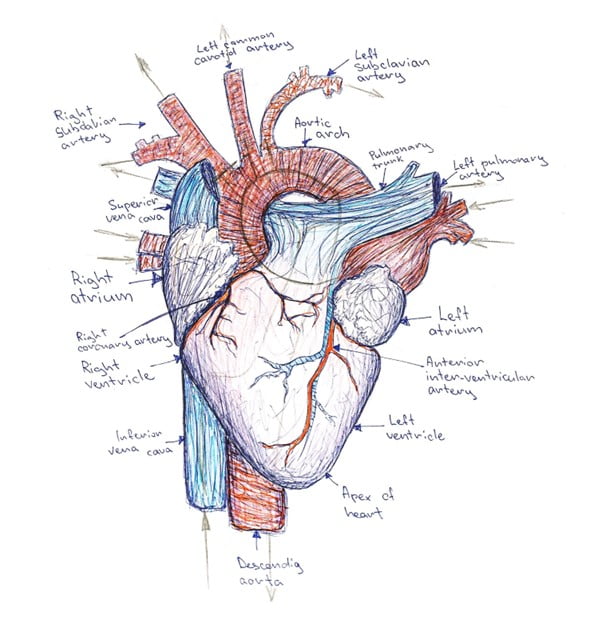
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. The anatomy of the heart includes several structures that work together to ensure that the heart functions properly.
The main structures of the heart include:
- The pericardium: This is a thin sac that surrounds the heart and helps to protect it.
- The myocardium: This is the muscular layer of the heart that is responsible for contracting and relaxing to pump blood.
- The endocardium: This is the inner lining of the heart that helps to prevent the blood from leaking out of the heart.
The heart has four chambers: the left and right atria and the left and right ventricles. The atria are the upper chambers of the heart, while the ventricles are the lower chambers.
The heart has four valves that help to ensure that the blood flows in the correct direction through the heart: the tricuspid valve, the mitral valve, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve.
The heart also has a network of blood vessels that carry blood to and from the heart. The arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while the veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Understanding the anatomy of the heart is important for diagnosing and treating heart conditions and for understanding how the heart functions.