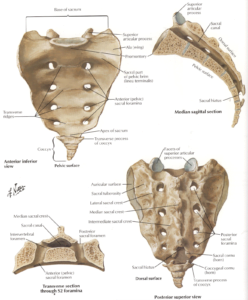
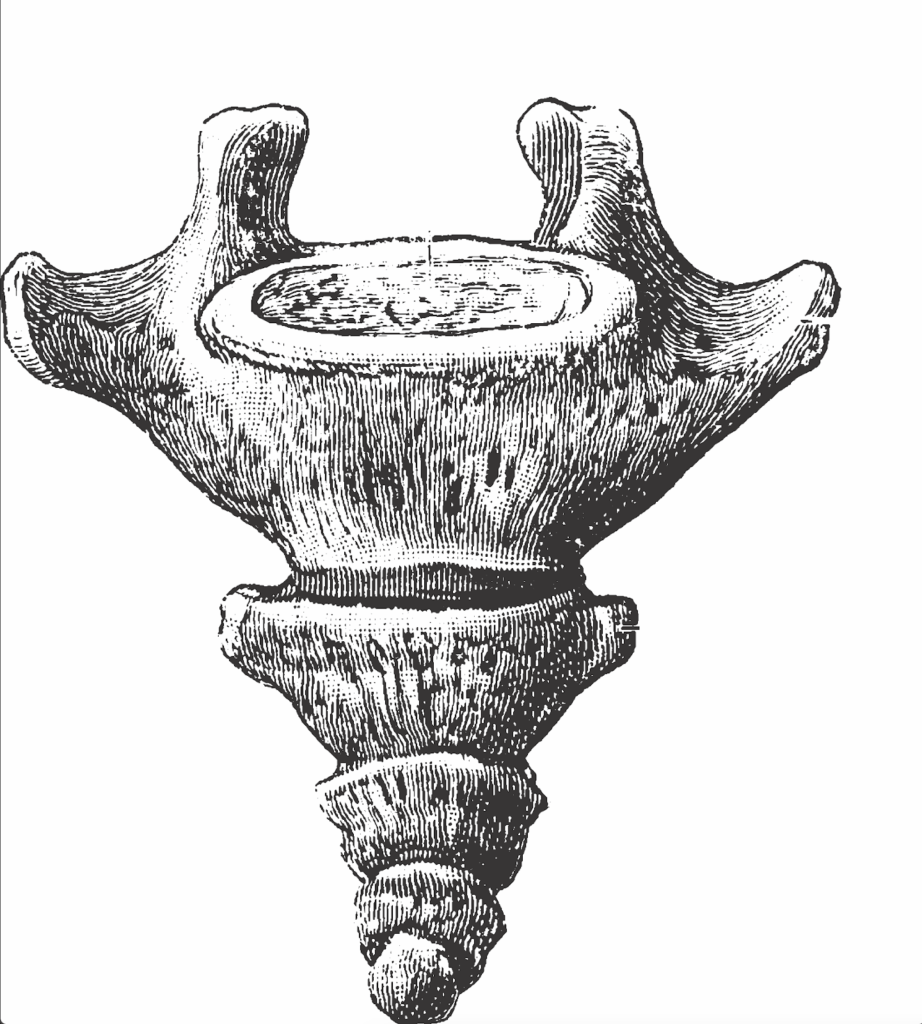
The coccyx, also known as the tailbone, is a small, triangular bone located at the base of the spine. It is made up of three to five small, fused vertebrae, and is located between the sacrum and the pelvis.
The coccyx serves as a point of attachment for several muscles and ligaments in the lower back and pelvis, including the levator ani muscle, which helps to support the pelvic organs. It also plays a role in weight-bearing and balance during sitting, as it is the point of contact between the spine and the chair or other surface.
Despite its small size, the coccyx is an important part of the skeletal system and plays a vital role in the function and stability of the lower back and pelvis. Injuries or disorders of the coccyx can lead to pain and discomfort, and may require medical treatment.
The coccyx serves several important functions in the body, including:
- Support: The coccyx provides support for the lower back and pelvis, and helps to distribute weight evenly when sitting.
- Attachment point: The coccyx is an attachment point for several muscles and ligaments in the lower back and pelvis, including the levator ani muscle, which helps to support the pelvic organs.
- Balance: The coccyx plays a role in balance and stability during sitting, as it is the point of contact between the spine and the chair or other surface.
Osteopathic treatment for disorders or injuries of the coccyx may include manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue massage, stretching, and joint mobilization to help relieve pain and improve mobility. Osteopathic practitioners may also use modalities such as heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to help manage pain and promote healing. It is important to work with a trained and licensed osteopathic practitioner to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.