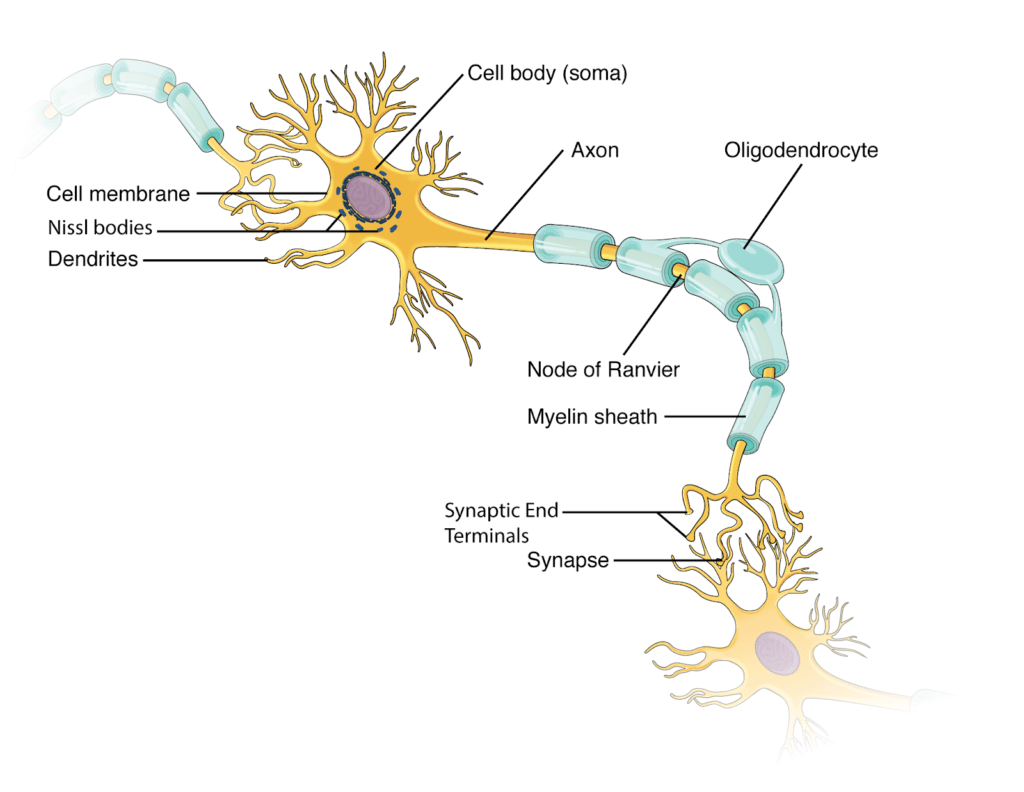
A neuron is a specialized cell that is responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. It is the basic unit of the nervous system and is essential for communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
The anatomy of a neuron consists of several different parts:
- Cell body: The cell body, also known as the soma, is the central part of the neuron and contains the cell’s nucleus and other organelles.
- Dendrites: Dendrites are short, branching processes that extend from the cell body and receive input from other neurons.
- Axon: The axon is a long, slender process that extends from the cell body and carries information away from the neuron.
- Myelin sheath: The myelin sheath is a layer of insulation that surrounds the axon and helps to protect and support it. It also helps to increase the speed at which information is transmitted along the axon.
- Synapse: The synapse is the small gap between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another. Information is transmitted across the synapse through the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
Neurons are essential for the transmission of information within the body, and their proper function is essential for overall health and well-being.